In this article:
What Is ECC Memory? ECC Memory Benefits
Assured Systems supply a wide range of products that support ECC and Non-ECC memory. Understand all you need to know about ECC Memory and its benefits.

With many of our customers asking about ECC memory, we have created an article to explain where it fits in the embedded and industrial computing market. While you’d assume that because both embedded and industrial computers in the market are built for high reliability that they’d implement ECC RAM to reduce system error. The Nuvo-8208GC GPU computer from Neousys is an example product which supports both Non-ECC and ECC memory.
What is ECC RAM or ECC Memory?
ECC RAM stands for ‘error-correcting code random access memory’. The ECC, or error-correcting code, refers to the memory components detection ability for mistakes that happen to occur in data memory without needing external computing resources. ECC RAM is very popular in servers or embedded systems with high-value data as it serves to protect against data corruption by automatically detecting and correcting memory errors.
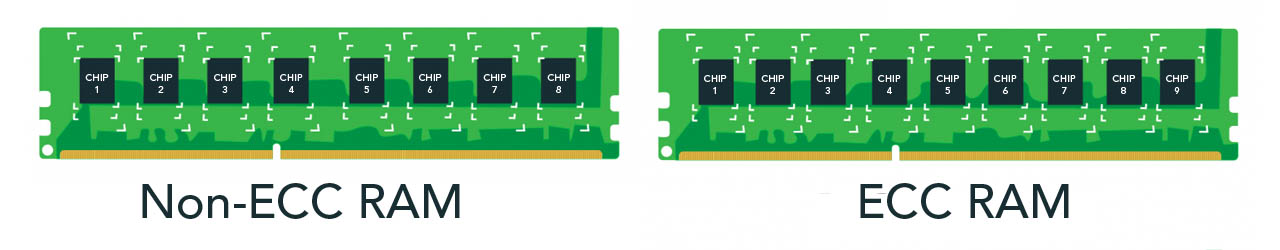
ECC vs Non-ECC RAM
Non-ECC Memory utilizes a bank of eight memory chips, in which data is stored and provided to the CPU on demand. Compared to Non-ECC memory, ECC memory is integrated with an additional memory chip which acts as both error detection and correction for the other eight memory chips.
To understand why you may or may not require error-correcting code RAM you must first understand the basic functionality of flash memory.
How does Flash Memory Work?
Flash chips are integrated with cells that have one of two states, state 0 or state 1. Flash cells require electricity to carry any state. Therefore, the computer will drive a level of power depending on whether your embedded system wants to code a 0 or 1 state to the memory. The memory controller then collates the state of each cell into a binary sequence, each binary string being unique. The collected binary sequence is then translated into computer data.
With volatile flash applications like computer RAM, the bank of cells always requires power to maintain their 0 or 1 state. When you switch off your computer the bank of cells on the RAM will clear. Static electricity can also cause a cell to flip states, 1 to 0 or vice versa. In effect, this will change the binary sequence and have a negative impact. Without going into binary too much, the number 135 is expressed as 010000111 in its binary string. If static electricity was to flip one of those cells, you could see the substantial effect on the single bit errors translated by the computer:
010000111 = 135
110000111 = 391
011000111 = 199
010100111 = 167
000000111 = 7
Memory flips can cause soft errors in performance which can be relatively harmless. For example, an average stick of 8 GB memory is known to see about 5 errors per hour of use, and for the average computer user, the impact of these errors isn’t perceptible. In the case of mission-critical applications on servers or industrial computers, these errors can quickly compound as system downtime from the operating system crashing or costly errors being caused by the wrong actions being carried out.
Benefits of ECC RAM
Mission critical applications are where the benefits of ECC memory comes to fruition. ECC RAM carries a built-in controller which includes a parity code, alternatively known as a Hamming Code. If one of the bits happens to error, the built-in controller can report the corrected error back to the host computer. An algorithm is used to write the data in a way that allows the formula to match correlating data. The Hamming Code algorithm can check for data integrity with a minimal amount of redundant data, in effect supporting computer RAM. If error rates are very high, then this method isn’t very useful.
When Should I Use ECC RAM and is ECC RAM worth it?
With a reduction in data error, integrating ECC memory in your computer system would seem the best way forward. Not all computer systems can support ECC RAM and requires a motherboard, chipset, and processor which supports the functionality. The extra memory cells and built-in controller also causes a 2-3% decrease in performance over Non-ECC RAM due to the resources required by the data processing Hamming Code algorithm.
If you have a mission critical embedded system susceptible to encountering memory errors then you should consider ECC memory and its ability in correcting data to help prevent data loss, expensive errors or system downtime. The small offset of increased investment in ECC memory and compatible components could save you in repairs down the line, keeping your production line operational and reducing hardware maintenance as intended. The increase in cost for ECC memory varies, but you should expect to pay on average between 10 and 20% more depending on the size of the memory stick. The larger the memory stick, the greater the increase in cost.










