In this article:
- Introduction
- Fan-cooled vs Fanless Industrial Computers
- Advantages of Fanless Industrial Computers
- Typical Heat Sink Design in Fanless Industrial Computers
- Applications of Fanless Industrial Computers
- Considerations for Fanless Industrial Computers
- Conclusion

Introduction
As computer technology advances, the need for effective cooling solutions becomes increasingly critical. Traditional fan-cooled systems, while effective at dissipating heat, introduce issues such as dust and debris accumulation, which can compromise the reliability and lifespan of the computer.
Fanless cooling methods significantly enhance the performance and reliability of industrial computers. This article explores why fanless industrial computers are preferred for harsh environment applications, highlighting their benefits and comparing them to traditional fan-cooled systems.
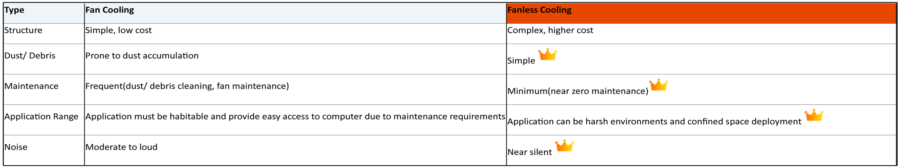
Fan-cooled vs Fanless Industrial Computers
Fan-cooled Industrial Computers
Fan cooling is the most common method for managing heat in computers. This method involves using fans to remove heat from the heatsink, expel hot air from within the computer, and draw in cooler air from the surroundings. While effective, fan-cooled systems have several drawbacks:
- Dust and Debris Accumulation: Fans draw in air from the surroundings, which often contains dust and debris. Over time, this can accumulate inside the computer, clogging components and reducing the efficiency of the cooling system.
- Increased Maintenance: To ensure optimal performance, fan-cooled systems require regular cleaning and maintenance to remove accumulated dust and debris.
- Noise: Fans generate noise, which can be disruptive in environments where quiet operation is essential.
- Space Requirements: Fans and the necessary airflow paths require additional space, making the overall system larger.
Fanless Industrial Computers
Fanless industrial computers utilise alternative cooling methods, primarily through strategic component placement and the use of increased-size heatsinks. These systems avoid many of the issues associated with fan cooling:
- Dust and Debris Resistance: The absence of fans means there is no mechanism for drawing in air, significantly reducing the risk of dust and debris entering the system. This enhances the computer’s reliability and longevity.
- Reliability: Without fans, there is no risk of mechanical failure related to the cooling system. Fanless designs are inherently more robust, offering higher reliability, especially in demanding 24/7 operations.
- Low Power Consumption: Fanless designs are more energy-efficient, as they do not require power for running fans. This reduces overall power consumption and deployment costs.
- Compact Size: The lack of fans allows for a more compact design, making fanless industrial computers ideal for installation in confined spaces such as cabinets, carriages, integrated automation equipment, or narrow gaps.
- Quiet Operation: The absence of fans results in near-silent operation, making these computers suitable for environments where noise reduction is important, such as hospitals and libraries.
- Maintenance: Fanless systems require less maintenance since there are no fans or air paths to clean, significantly reducing downtime and improving convenience.
Advantages of Fanless Industrial Computers
Fanless industrial computers offer several advantages over their fan-cooled counterparts:
Dust and Debris
The fanless design minimises the entry of dust, debris, and other foreign objects. This reduces potential damage and maintains efficient heat dissipation, crucial for environments where cleanliness cannot be guaranteed, such as factories and outdoor installations.
Reliability
Without fans, fanless industrial computers are less prone to dust accumulation and reduced heat dissipation efficiency. This leads to a lower failure rate and makes them suitable for continuous, 24/7 operation. Their robust design ensures they can withstand the rigours of harsh environments.
Low Power Consumption
Fanless designs focus on minimising heat generation, resulting in lower overall power consumption. This not only reduces energy costs but also decreases the thermal stress on components, further enhancing reliability.
Compact Size
The elimination of fans allows for a more compact design. This makes fanless industrial computers ideal for applications where space is limited, such as inside control cabinets, vehicle interiors, and other confined spaces.
Near Silent Operation
The absence of moving parts like fans makes these computers almost silent during operation. This is particularly advantageous in environments where noise needs to be kept to a minimum, such as in medical facilities, libraries, and offices.
Reduced Maintenance
Fanless systems do not require regular cleaning and maintenance related to fans and air paths. This results in less downtime and lower maintenance costs, making them more convenient for users and more economical over their lifespan.
Typical Heat Sink Design in Fanless Industrial Computers
The heatsink is a critical component in fanless industrial computers, responsible for dissipating heat generated by the computer’s components. A typical heatsink design involves several key elements:
- Materials: The most common materials used for heatsinks are aluminium and copper. Aluminium is lightweight, cost-effective, and has good thermal conductivity, making it a popular choice. Copper, while more expensive and heavier, offers superior thermal conductivity and is often used in high-performance applications.
- Fins: The heatsink is usually designed with multiple fins to increase the surface area available for heat dissipation. These fins are typically thin and closely spaced to maximise the contact area with the surrounding air.
- Base: The base of the heatsink, which is in direct contact with the heat-generating components, is designed to ensure maximum thermal conductivity. It is often polished to a smooth finish to improve contact and heat transfer efficiency.
- Heat Pipes: Some heatsink designs incorporate heat pipes, which are sealed tubes filled with a working fluid. These pipes help transfer heat from the base of the heatsink to the fins more effectively.
- Shape and Size: The shape and size of the heatsink are tailored to fit the available space within the computer and to maximise airflow around the fins. Heatsinks may be designed in various shapes, including rectangular, cylindrical, or custom shapes to fit specific applications.
Placement
The placement of the heatsink is strategic, ensuring that it directly contacts the components that generate the most heat, such as the CPU, GPU, and power supply units. The heatsink is mounted using thermal interface materials (TIMs) like thermal paste or pads to enhance heat transfer between the component and the heatsink.
Applications of Fanless Industrial Computers
Fanless industrial computers are ideal for a variety of applications in harsh environments due to their durability and reliability. Some common industries and applications include:
Semiconductor Manufacturing
In semiconductor manufacturing, clean environments are essential. Fanless computers minimise the risk of contamination, ensuring reliable operation in clean rooms and other controlled environments.
Automobile Manufacturing
The automotive industry often requires computers that can operate in environments with high levels of dust and vibrations. Fanless industrial computers meet these demands, providing reliable performance on factory floors and in vehicle testing areas.
Public Transportation
Public transportation systems, such as buses and trains, require computers that can withstand constant movement, vibration, and varying temperatures. Fanless designs ensure continuous operation without the need for frequent maintenance.
Energy Management
In energy management systems, especially in remote or outdoor locations, reliability and low maintenance are crucial. Fanless computers can operate in a wide range of temperatures and conditions, making them suitable for monitoring and control applications in the energy sector.
Smart Agriculture
Agricultural environments expose equipment to dust, moisture, and varying temperatures. Fanless industrial computers are robust enough to handle these conditions, providing reliable performance for automated farming and monitoring systems.
Smart Cities
Urban infrastructure requires reliable computing solutions for applications such as traffic management, surveillance, and public information systems. Fanless industrial computers offer the durability and low maintenance needed for these critical applications.
Considerations for Fanless Industrial Computers
Heat Dissipation and Overheating Concerns
A common concern about fanless industrial computers is the potential for overheating. While any computer can overheat if not properly designed, fanless industrial computers are engineered with advanced heat dissipation techniques to manage thermal loads effectively. These systems use efficient heatsinks, thermal pads, and strategic component placement to ensure they operate within safe temperature ranges. Fanless systems with robust thermal management ensure stable operation even in extreme conditions, preventing overheating and maintaining performance.
Suitability for Industrial Applications
Fanless industrial computers are particularly recommended for industrial applications due to their resilience to harsh environments. These applications often involve exposure to dust, vibrations, and extreme temperatures, conditions that fan-cooled systems would struggle to endure. Fanless designs eliminate the risk of mechanical failure associated with fans, making them highly reliable for continuous operation. Their compact form factor allows easy installation in space-constrained environments, such as control cabinets and machinery.
Industries Benefiting from Fanless Designs
Various industries benefit from the robustness and reliability of fanless industrial computers. In semiconductor manufacturing, these systems provide clean operation without the risk of contamination. The automotive industry values their durability in dusty and vibration-prone environments. Public transportation systems rely on their continuous operation capabilities. Energy management applications appreciate their reliability in remote and outdoor settings. In smart agriculture, fanless designs ensure reliable performance despite exposure to dust and moisture. Smart cities utilise these computers for critical infrastructure applications, benefiting from their low maintenance and high reliability.
Deployment in Semi-Outdoor Areas
Fanless industrial computers can be effectively deployed in semi-outdoor areas, provided they are designed to withstand environmental conditions such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, salinity, vibration, and chemical exposure. For enhanced protection, selecting computers with IP66/IP67/IP69K ratings is recommended. Assessing the specific conditions at the deployment site ensures that the chosen computer specifications match the required protection level.
Conclusion
Fanless industrial computers offer significant advantages for harsh environment applications, including enhanced reliability, low maintenance, and compact design. Their ability to operate in dusty, dirty, and vibration-prone environments makes them ideal for a wide range of industrial applications. By eliminating the need for fans, these computers provide a robust and reliable solution that reduces downtime, extends system lifespan, and lowers operational costs. Whether in manufacturing, transportation, energy management, or smart cities, fanless industrial computers are the preferred choice for demanding applications.










